Table Of Content

Scaffolding, too, can cost millions to erect around tall Gothic buildings to reach areas needing repair. With only limited public funds available, the steep costs of Gothic restoration often rely heavily on private donations and charity foundations. Fundraising typically cannot provide the full extent needed for ongoing maintenance. Gothic architecture reflected the cultural and social values of the High and Late Middle Ages in Europe through its grand scale, verticality, light, and focus on the divine. Gothic cathedrals also expressed civic pride, as each town sought to outdo others with the tallest spire, largest windows, and most ornate carvings.
Barcelona Cathedral – Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain
Politically, this era was marked by peaceful and prosperous times, where buildings were carefully designed and took up to a century to construct as a result. Vienna, the former capital of the once-mighty Hapsburg Empire, was a leading city in central Europe during the Middle Ages. Saint Stephen’s Cathedral is Vienna’s most important church and is a testament to the complex history of the city. Like a lot of cathedrals of the era, the church was built over centuries, with construction starting and stopping sporadically. The cathedral features two Romanesque towers, which were built prior to the gothic nave. The south tower was the tallest structure in the city for hundreds of years, and work was started on a similar north tower but was never completed.
Span of Gothic Architecture
Other influences that drove the construction of more Gothic structures were the rise in wealth and population numbers, resulting in churches and cathedrals needing to be built larger in order to accommodate the influx of pilgrims. Gothic architects wanted to express the grandeur and power of the rise in the nation’s prosperity in their buildings. Gothic architects have incorporated the style into many types of buildings such as Gothic churches and Gothic cathedrals, parish churches, abbeys, palaces, castles, universities, and town halls.
Flying Buttresses
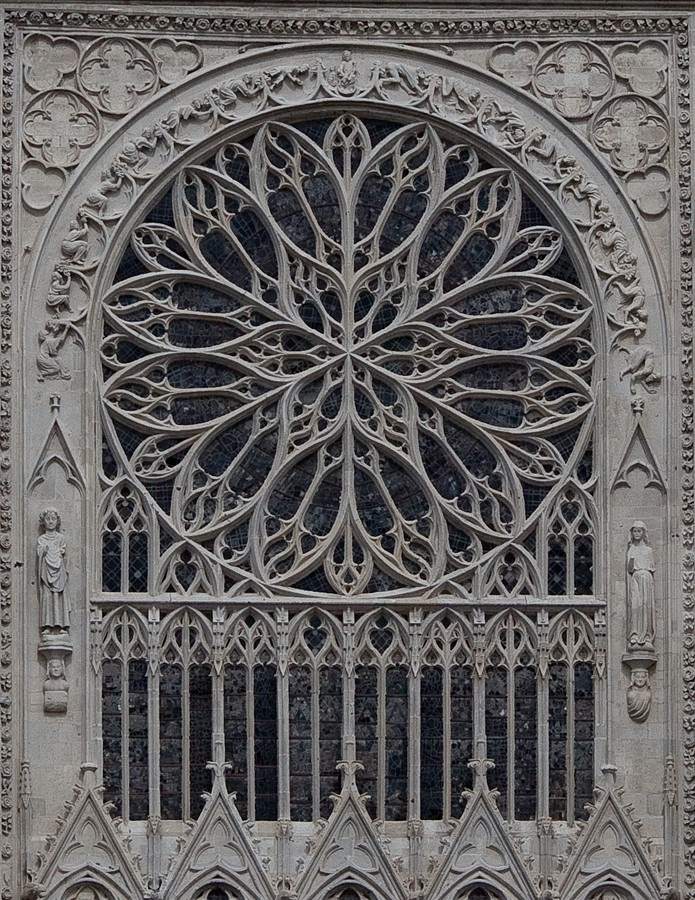
The most significant and impressive characteristic of the Gothic architecture style is the pointed arches. The pointed arches were also used for construction purposes, such as to bring transverse vaults equal to the height of diagonal vaults. Gothic architecture is a style of architecture that flourished in Europe during the late medieval period, from the 12th to the 16th century. It originated in France in the 12th century and spread throughout Europe, becoming the dominant architectural style for many centuries. The term “Gothic” was originally used as a pejorative term by Renaissance architects, who considered it a deviation from the classical architecture of ancient Rome and Greece.
Here at Reims Cathedral, the roof is supported by much larger buttresses than what was found in Early Gothic Buildings. The arches connect to columns that are several feet from the exterior walls, and then those columns transfer the loads to the ground. The Facade of Reims Cathedral also combines a Rose Window, Pointed Arches, and intricate detailing to create one of the most famous Gothic Elevations in all of France.
Digital mapping and augmented reality offer new interpretations of Gothic sites, overlaying virtual elements onto physical buildings to show their original appearance or construction sequence. Smartphone apps utilize augmented reality at sites like Milan Cathedral and Chartres Cathedral. Common examples are found in Christian ecclesiastical architecture, and Gothic cathedrals and churches, as well as abbeys, and parish churches. It is also the architecture of many castles, palaces, town halls, guildhalls, universities and, less prominently today, private dwellings. Many of the finest examples of medieval Gothic architecture are listed by UNESCO as World Heritage Sites.
The Veronicas - Gothic Summer - 360 MAGAZINE - GREEN DESIGN POP NEWS - 360 Magazine
The Veronicas - Gothic Summer - 360 MAGAZINE - GREEN DESIGN POP NEWS.
Posted: Mon, 19 Feb 2024 08:00:00 GMT [source]
Neo-Gothic Architecture

Parler and his workshop designed many other buildings and cathedrals across central Europe. Most of the stained glass that was originally installed is still intact in this remarkably well-preserved and maintained building. The windows of the building are considerably large, which was made possible by the use of heavy flying buttresses on the exterior. The cathedral has been a point of pilgrimage for many Christians since the 12th century due to the church being in possession of the Sancta Camisa, believed to be a piece of clothing worn at Christ’s birth by his mother, Mary. The flying buttresses of the Gothic style were more complex and often had arches of varying sizes that each connected to various levels of the structure.
Structures with similarly precise vaulting and chains of windows along the perimeter were soon begun with Notre-Dame de Paris (begun 1163) and Laon Cathedral (begun 1165). By this time it had become fashionable to treat the interior columns and ribs as if each was composed of a bunch of more slender parallel members. The columns and arches used to support these different elevations contributed to the severe and powerfully repetitive geometry of the interior. Window tracery (decorative ribwork subdividing a window opening) was also gradually evolved, along with the use of stained (coloured) glass in the windows. The typical French early Gothic cathedral terminated at its eastern end in a semicircular projection called an apse.
Unlock the World of Decorative Arts
St. Stephen’s Cathedral is situated in Vienna, Austria, and is regarded to be the most prominent Gothic structure in the whole city. The building of the church was first initiated by Duke Rudolf IV and was designed by Anton Pilgrim. Much of the requirement for more light was based on literal interpretations of theological doctrines, and new improvements regarding technical elements such as buttresses and vaults allowed for larger and higher windows than before. Yet, in some places like Belgium and England, the Gothic style would continue and evolve well into the 16th century. From the mid-18th century into the 20th century, there were a series of revivals of Gothic-style architecture, mostly used in the designs of university buildings and churches. Its prime era was the late 12th to the 16th century, but it continued in some areas into the 17th and 18th centuries.
Instead of the round arches, which were characteristic of the Romanesque buildings, architects using the gothic style adapted the tall thin pointed arches found in Islamic architecture. This profile highlighted each cathedral's height by pointing towards the sky and accommodating a vaulting in a similar shape. Gothic designs were actually created to bring more sunlight into spaces, mainly churches, and led to the design and construction of some of the world’s most iconic buildings.
Reflective pools, fountains and small ponds can add an element, evoking the introspective and melancholic themes found in gothic literature. You also can incorporate dark delights such as pottery and statuary and consider up-lighting trees for evening ambiance. Withered plants and faded blooms contribute to the thematic experience, giving you an excuse to let the garden get away from you this year.
Evolving from Romanesque architecture, this medieval aesthetic features vaulted ceilings, exaggerated arches, flamboyant windows, and pointed arches, alongwith appreciated humongous scales and grandeur. However, there was one thing different.Abandoning the adaptation of thicker walls, Gothic architecture features a framework employing flying buttresses, defying the conventional laws of structural reinforcement. The designers advocating for this style chose thinner walls and touched newer skylines with the urban context. The use of stone structures allowed the architects of the time to evoke ethereality in magnificence and form purposeful characters. Originating in the early 12th century in Northwest England and France, the Gothic Era further expanded to Latin Europe in the 13th century.